🐍 Create Virtual Environment and Use requirements.txt in Django
Want to start a Django project and manage your packages properly? Here’s how to create a virtual environment and use requirements.txt.
🧪 1. Create Virtual Environment with python -m venv
- Open your terminal
- Go to your project folder
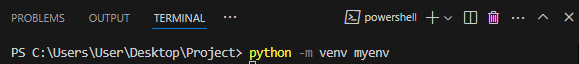
- Run the command
python -m venv myenv
💡 Note for Mac users: On macOS, use python3 -m venv myenv instead of python.
📌 Why Use a Virtual Environment?
Virtual environments keep your project’s packages isolated. It also:
- Prevents conflicts between different projects
- Lets you use different versions of the same package
- Makes it easier to manage dependencies
🧠 2. Activate the Virtual Environment
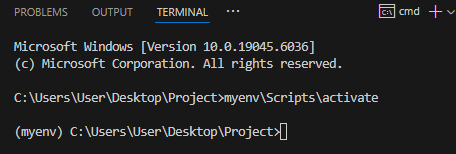
- On Windows:
myenv\Scripts\activate
- On Mac/Linux:
source myenv/bin/activate
- You will see
(myenv) at the beginning of the terminal line
✅ Final Step
Now that your environment is active, you can install packages like Django using pip. For example:
pip install django
💡 Note for Mac users: On macOS, use pip3 install django instead of pip.
🔐 Safety Tip
To save your installed packages, use this:
pip freeze > requirements.txt
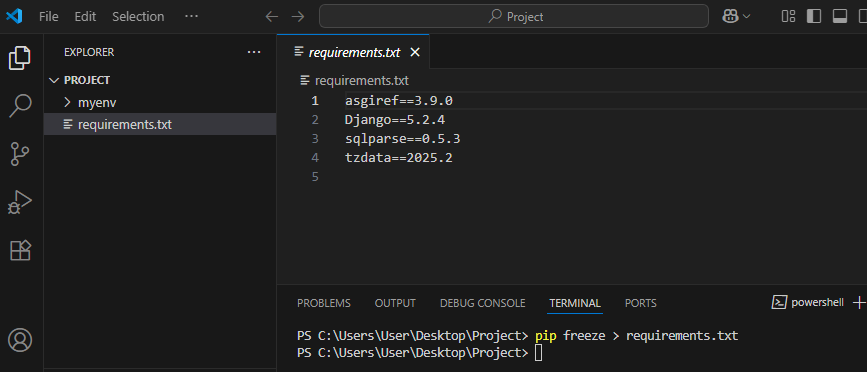 This will create a requirements.txt file that lists all dependencies. You can install them later with:
This will create a requirements.txt file that lists all dependencies. You can install them later with:
pip install -r requirements.txt
💡 Mac users: Again, use pip3 install -r requirements.txt if needed.
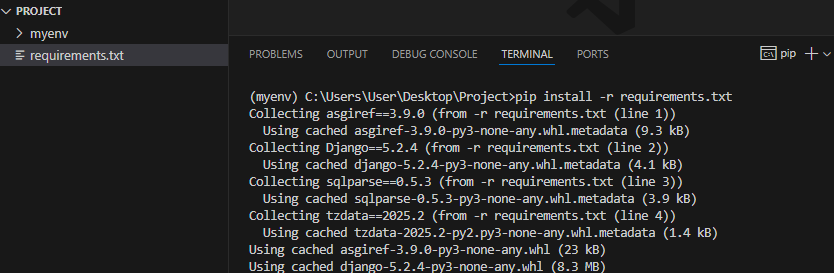


 This will create a requirements.txt file that lists all dependencies. You can install them later with:
This will create a requirements.txt file that lists all dependencies. You can install them later with:
